Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Prev Med Public Health > Volume 54(4); 2021 > Article
-
Scoping Review
The Most Important Social Determinants of Slum Dwellers’ Health: A Scoping Review -
Farhad Nosrati Nejad1
 , Mohammad Reza Ghamari2
, Mohammad Reza Ghamari2 , Seyed Hossein Mohaqeqi Kamal3
, Seyed Hossein Mohaqeqi Kamal3 , Seyed Saeed Tabatabaee4
, Seyed Saeed Tabatabaee4 , Raheleh Ganjali5
, Raheleh Ganjali5
-
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health 2021;54(4):265-274.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3961/jpmph.21.073
Published online: July 8, 2021
1Social Determinants of Health Research Center, University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences, Tehran, Iran
2Department of Social Welfare Management, University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences, Tehran, Iran
3Social Welfare Management Research Center, University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences, Tehran, Iran
4Social Determinants of Health Research Center, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran
5Clinical Research Unit, Faculty of Medicine, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran
- Corresponding author: Mohammad Reza Ghamari Department of Social Welfare Management, University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences, P.O. Box 1985713834, Tehran, Iran E-mail: mrg1400@gmail.com
Copyright © 2021 The Korean Society for Preventive Medicine
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Objectives
- Given the importance of social determinants of health in promoting the health of slum residents, this study was conducted with the aim of identifying the main dimensions and components of these determinants.
-
Methods
- This scoping review study was conducted according to the PRISMA-ScR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews). A comprehensive search was performed of PubMed, ProQuest, Scopus, and Web of Science for articles conducted from 2010 to the end of 2019. Studies were selected based on inclusion criteria, with a special focus on studies dealing with the social determinants of physical and mental health or illness.
-
Results
- Thirty-three articles were selected to extract information on the social determinants of health. After reviewing the articles, 7 main dimensions (housing, socioeconomic status of the family, nutrition, neighborhood characteristics, social support and social capital, occupational factors, and health behaviors) and 87 components were extracted as social determinants of health among slum dwellers.
-
Conclusions
- This framework could be used by planners, managers, and policy-makers when making decisions affecting the health of these settlements’ residents due to the common characteristics of slums around the world, especially in developing countries.
- Keywords: Social determinants of health, Poverty areas, Developing countries, Slum
- According to the United Nations Center for Human Settlements, an informal settlement is a time-worn area of a city, known for low-quality housing construction, unsafe residential conditions, pollution, overcrowding, and a lack of basic facilities [1]. International organizations have estimated that more than 1 billion people (about 32% of urban communities) live in slums. This living arrangement has grown worldwide since the 1990s, and the number of people living in slums is expected to exceed 2 billion by 2030 [2].
- Slums have some characteristics in common; they are areas where there may be proximity effects facilitating the impact of factors such as environmental pollution, massive waste, overcrowding, non-standard houses, and physical hazards (such as accidental burns and fires), on residents’ health [3]. The accumulation of problems in these areas endangers the physical, mental, and social health of these areas’ residents. Studies have shown that the health status of people living in slums is much worse than that of those living in adjacent urban areas [4].
- Addressing the health of the residents of these areas only by providing health services would not be successful [5]. To improve the health of people living in the outskirts of cities, it is necessary to find determinants that have a major impact on health, as focusing on these determinants could improve the health status of these areas’ residents. It seems possible that by improving the social and environmental conditions of slums using the analytical framework of social determinants of health, the physical, mental, and social health status of residents could be improved [4].
- Various studies have emphasized the important role of social determinants of health in the development/eradication of diseases and in the design of necessary interventions based on these determinants. Pawar et al. [6] noted that appropriate interventions to improve the health of slum dwellers need to be designed and implemented based on a correct understanding of the factors affecting health. Social factors are as important as physical factors in determining the health status of residents and the type of interventions that would be appropriate to propose; in other words, public policy that seeks to achieve continuous improvement in social determinants of health, such as income, education, housing, food, security, and neighborhood status, could have positive and long-lasting effects on people’s health [7].
- There are various models for social determinants of health, and the World Health Organization (WHO) has also proposed a significant model in this regard [8,9]; however, despite the common features of slums and the difference in the health status of people residing in these areas and other places, no model focusing on slums has been proposed based on the available evidence and studies.
- Given the importance of social determinants of health and their role in the health of slum dwellers, and also in light of the fact that in recent years, several studies have been conducted in different parts of the world to identify social determinants of health among slum dwellers, the main purpose of this study was to extract social determinants of health from various studies conducted in the last decade on people living in slums and provide a comprehensive framework of social determinants of health with dimensions and components affecting health.
- This framework could be used by planners, managers, and policy-makers when making decisions affecting the health of these settlements’ residents due to the common characteristics of slums around the world, especially in developing countries.
INTRODUCTION
- This scoping review study was conducted according to the PRISMA-ScR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses Extension for Scoping Reviews) [10] to identify and extract the most important dimensions and components of social determinants of health from various studies conducted in this field without considering and evaluating the methodological quality of the included studies; thus, this study is considered to be a scoping review [11].
- Data Sources and Search Strategy
- A scoping search was performed in PubMed, ProQuest, Web of Science, and Scopus to find articles published during 2010-2019. The search was performed from November 5, 2019 to December 15, 2019. In order to search for studies conducted on social determinants of health among residents of slums, the search domain was first identified from the PubMed site, and then keywords and related words were identified and extracted from various sources. A comprehensive search was performed of the aforementioned databases using different combinations of keywords and Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms. Table 1 summarizes the keywords and MeSH terms used in this study.
- Eligibility Criteria
- Given that the social determinants of health in slums could be either the determinants of a particular disease or the social determinants of health in general, the inclusion criteria for studies to be included in this survey were as follows: (1) studies published in scientific journals, (2) studies published during 2010-2019, (3) studies published in English, (4) studies investigating social determinants of physical and mental health, (5) studies that pointed to social determinants of any type of mental or physical illness, and (6) studies whose full text was available for data extraction.
- The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) conference papers, (2) studies in languages other than English, (3) studies whose full-text was not available, and (4) studies that were conducted on health or diseases in slums but had no relation to social determinants of health.
- Data Extraction
- At first, the selection was based on each article’s title and abstract in order to identify the articles related to the research question domain. Next, articles were selected based on inclusion criteria with a special focus on studies dealing with the social determinants of physical and mental health or illness. After these 2 steps, the full text of the remaining articles was reviewed for further investigation and extraction of determinants reported to affect health.
- A special spreadsheet was designed to systematically extract data from the selected studies. The data extracted from the studies were related to the determinants of physical and mental health or physical and mental illness. The data were screened by the corresponding author (MRG) and then revised and confirmed by the second and third reviewers (FNN and SHMK).
- Synthesis and Analysis
- The social determinants of health or illness in slums mentioned in the articles were extracted using the data collection forms. After extracting and entering the data in the prepared forms, the data were summarized in terms of similarity and categorized based on the experience and expertise of 2 experts (FNN and SHMK).
- Social determinants of health are defined as the social conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and grow old. They are social characteristics that are present or occur in the place of residence [8]. The concept of social determinants of health refers to the factors that help people stay healthy until they get sick and receive services.
- Social determinants of health include both the specific characteristics of a social context affecting health and the mechanisms by which social conditions affect health. Significant social determinants are those that could potentially be changed by conscious actions.
- It is now believed that social factors affecting health, such as income level, education level, occupational factors, nutrition, social class, unemployment, and childhood experiences, are more important than biological factors for the occurrence of diseases, and if ignored, it will be impossible to achieve the goals of the health sector and establish justice in health [9].
- Ethics statement
- In this study, we strived to use the data properly and without prejudice as much as possible. Ethics approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences (Ethical code: IR.USWR. REC.1398.165).
METHODS
- Study Selection
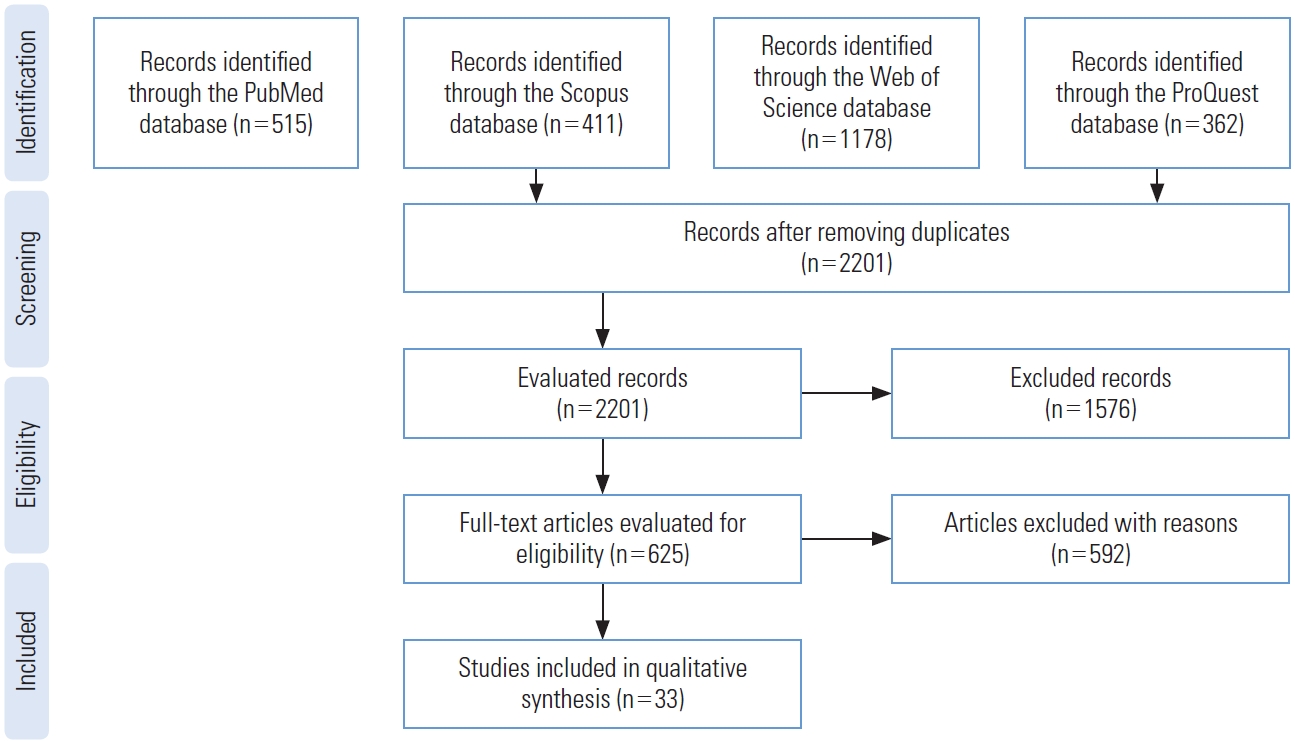
- The data collected from the aforementioned databases were as follows: 515 records from PubMed, 411 records from Scopus, 1178 records from Web of Science, and 362 records from ProQuest. After eliminating duplicates, 2201 records were retrieved. By evaluating the titles and abstracts of the studies and by taking into account the inclusion criteria, 625 papers were selected for full-text evaluation, while 1576 papers did not meet the inclusion criteria. In the full-text evaluation stage, 592 papers were eliminated based on the exclusion criteria, and 33 studies remained for further evaluation (Figure 1).
- Characteristics of the Sources of Evidence
- Table 2 presents the general characteristics of the 33 selected studies [2,3,12-42]. The oldest study was published in 2012, and the most recent study was published in 2019. Among the studies reviewed, 10 were cross-sectional studies [17,21,22,24,26,31,32,35,37,42], 6 were literature reviews [2,14,18,19,34,39], 5 were secondary analyses, 4 used mixed methods, and 8 studies were designed using other methods, as listed in Table 2. Eight studies were conducted in India [15,17,19,24,26,37,41,42], 7 studies were conducted in Bangladesh, 2 studies were conducted in Jordan, and the rest of the studies were carried out in various other countries (Table 2).
- Synthesis of Results
- After conducting the research steps, the social determinants of health extracted from the studies were divided into 87 components and the following 7 main dimensions: housing, socioeconomic status of the family, nutrition, neighborhood characteristics, social support and social capital, occupational factors, and health behaviors. In addition, the extracted components that were repeated in several articles, as well as the number of their repetitions as an indicator of their importance, were also identified.
- The most important dimensions and components of social determinants of slum dwellers’ health, mentioned in the studies reviewed, are as follows:
- Housing and its conditions, as mentioned in the reviewed studies, are one of the most important determinants of slum dwellers’ health. The structure of housing is associated with certain health consequences, and the improvement of housing status over time affects the health of residents [12]. The components of the housing dimension identified in some of the reviewed studies as factors affecting health are as follows:
Physical structure of housing, lack of strength, durability, and safety of buildings due to the use of brittle, non-durable, and flammable materials [2,12,13,23,34]; Indoor air pollution and poor ventilation [2,35]; The presence of small rooms in houses [13,14]; Unhygienic toilets [13]; Lack of security and fear of destruction due to illegal construction [13,14]; Contamination with rodents and insects [14]; Adverse social-psychological residential environment [12,18,29,34]; The use of pathogenic and toxic substances in the construction of houses such as asbestos and lead [14]; House seizure (rent, private property, etc.) [36].
- Socioeconomic characteristics of the family, as one of the most important dimensions of social determinants of slum dwellers’ health, encompass different components, mentioned in some of the reviewed studies as factors affecting health. These components are as follows:
Parental education level, lack of formal education [13,16,17,19,24,26,27,29,31-34,36,39,40]; Family income, poverty in the family, income insecurity, financial pressure, dissatisfaction with the family’s financial situation [13-15,17-19,23-25,28-30,33-36,42]; Family size, overcrowded and dense family space [14,27,35,36,41]; Family religion [17,27,41]; Family type (nuclear, extended, single-parent) [28,35,41]; Length of stay in the neighborhood [27]; Violence, gender discrimination, unfair behaviors, and misbehavior against women in the family [13,29,39]; Violence, gender discrimination, and unfair behaviors against children in the family [13,29,39]; Gender and age of family members [17,18]; Family cultural hobbies (the use of media, reading, etc.) [17,27]; Family wealth status [16,22,27,40]; Family race and ethnic group [18,28]; Limited travel [13]; Being covered by family support institutions [12]; Having fights, misunderstandings, and conflicts in the family [24,37]; Undesirable childhood experiences [34].
- The components of the nutrition dimension, identified in some of the reviewed studies as factors affecting health, are as follows:
Malnutrition, inadequate and poor diet, and micronutrient deficiencies [13,29,30]; Obesity [24]; Weak and thin family members [13]; Food contamination [30]; Improper selection of healthy foods [19]; Family food insecurity [15,22,34]; Nutritional habits (such as regular consumption of fast food, the number of times one eats vegetables, fruits, and meat) [24,35]; Low-birth-weight babies [13].
- One of the most important dimensions of social determinants of health, which significantly differs in slums from other urban areas and should be given special attention, is neighborhood characteristics, which encompass many components, as follows:
Lack of access to public resources (parks, green space, museums, libraries) ]20,28]; Lack of access to spaces for sports [13]; The presence of stray dogs and livestock in the neighborhood, density of mice [13]; Conflict, such as being annoyed and harassed by neighbors [28]; Lack of access to safe, high quality, and hygienic drinking water [13,19,31, 35]; Noise pollution [28]; Environmental pollution of the place of residence, lack of cleanliness and poor sanitation of neighborhoods [13,14,30]; Lack of street lighting [13]; Existence of industrial pollution in the neighborhood [13]; Existence of unprotected hazards (such as railways and power lines) [13,28]; Lack of educational facilities and schools and low quality of education [30,39]; Inadequate and insufficient public health facilities located at long distances [14,16,27,29,38,39]; Insecure public space due to gang crime and conflicts, neighbors’ crime and conflicts [14,30,39]; The quality of service delivery organizations in the neighborhood, such as stores, pharmacies, banks, and offices, and their long distances [28]; Lack of private-sector health facilities [38]; Lack of charitable and non-governmental health facilities [38]; Lack of places for recreation [35,39]; Inappropriate public transportation network and difficulty in accessing public transportation [2,13,19, 28,31]; Physical hazards such as flood, subsidence, and fire [2,14,23]; Improper disposal of waste, environmental pollution with waste, and waste-transfer stations [13,27,38]; Inappropriate and open sewer systems [13,14,31,38]; Very high population density in the neighborhood [2,13,23]; Air pollution [28]; Unpaved and dirt alleys [13]; Narrow and irregular alleys [13]; Lack of water and electricity supply, informal use of water and electricity resources [13,29]; Notoriety of the neighborhood [2,18]; Lack of access to police services [28].
- The components of the health behaviors dimension, identified in some of the reviewed studies as factors affecting health, are as follows:
Not performing health screening and annual tests [29]; Not taking care of personal hygiene such as bathing, nail trimming, and tooth-brushing [23,35]; Addiction of a family member to drugs or alcohol [37]; Parental insensitivity to family health [36]; Excessive smoking [24,31]; Insufficient physical activity [19,24]; Stress [29,39]; Low individual health literacy [12,23,36,39]; Low environmental health literacy [23].
- Issues related to social protection, social exclusion, and social capital were also addressed in some of the reviewed studies as factors affecting the health of residents. These factors are as follows:
Social support, the number and presence of friends and relatives in the neighborhood, and having a large family [13,18,28,39]; Social capital, social cohesion and solidarity, and solidarity at the neighborhood level such as closeness to neighbors [12,14,18,25,28]; The degree of cooperation and mutual cooperation with neighbors, such as taking care of each other’s property [28]; Weakness and insignificance of traditional values [39]; Feeling discredited due to living in an illegal place [13]; The degree of belonging to the neighborhood [13]; Social rejection or deprivation and family isolation [13,15,25,29,34]; Social participation, engaging in civic activities, membership, and participation in groups and institutions such as mosques, social organizations, and non-governmental organizations [27,28,37]; Discrimination and perceived discrimination [18,34]; Low participation in religious ceremonies [37].
- The components of the occupational factors dimension, identified in some of the reviewed studies as factors affecting health, are as follows:
Job satisfaction [23]; Whether the mother and father are employed or unemployed [13,18,24,26,29,34,36,39]; Job type (such as having informal and non-productive jobs) [13,33]; Workplace conditions [13]; Long working hours with very low salary and income, especially for women and children [13]; Job insecurity [2,13,34].
RESULTS
Housing
Socioeconomic status of the family
Nutrition
Neighborhood characteristics
Health behaviors or high-risk and harmful behaviors for health
Social support, social capital, and deprivation
Occupational factors
- Residents of slums are faced with increased risks of disease and illness. According to the Commission on Social Determinants of Health, the living environment plays an essential role in the formation and determination of health and well-being [12]. In slums, a fully-shared physical and social environment is likely to have strong proximity effects and play a key role in the health of residents as a social determinant of health [3]. Many studies have been conducted to determine the most important determinants affecting people’s health, and different models have been proposed regardless of location [8,9]. In this study, the most important determinants of health in slums, which have distinctive features from other urban areas, were collected from various studies and presented as a basis for improving the health of these settlements’ residents. The main determinants were housing, socioeconomic status of the family, nutrition, neighborhood characteristics, social support and social capital, occupational factors, and health behaviors.
- In the most recent model of social health determinants presented by the WHO—which deals with the dimensions of social determinants of health in general, and not social determinants of health among slum dwellers—these determinants have been divided into 2 categories: structural and intermediate [9]. The identified determinants in this study, mostly derived from evidence-based research, are largely consistent with those included in the model presented by WHO and cover a wide range of determinants. However, a different classification was proposed for social determinants of health among residents of slums, because the model presented in this study focuses more on intermediate determinants and living conditions identified in the studies reviewed, while the WHO model focuses more on structural determinants such as governing and policy-making, perhaps because it is easier for studies to intervene on intermediate determinants. In a study by Lilford et al. [3], a different classification was presented for social determinants of health among residents of slums compared to this study. The presence of multiple classifications could lead to the analysis of the issue from different viewpoints, facilitating the design of appropriate interventions. A comparison of the dimensions and components identified in this and other studies showed that although the identified items were mentioned in various studies, their importance and order in studies were different.
- In a study by Nekoei-Moghadam et al. [13], housing was identified as a subset of the main determinants, which is inconsistent with the present study results. Given the importance of housing and its components mentioned above, it is one of the most important factors that should be taken into account when designing health promotion interventions for slum dwellers. For example, Alaazi and Aganah [14] noted that a lack of housing security due to the threat of slum cleansing was a well-known social-psychological stressor affecting the physical and mental health of African slum dwellers.
- According to Pawar et al. [6], the most important determinants of diseases among slum dwellers are age, education, social class, family type, and socioeconomic status of the family. In a study by Subbaraman et al. [15], it was noted that low family income and the problems related to living in slums were associated with mental disorders. According to the findings of this study, the family income component repeated in various sources is one of the most important and influential components affecting the health of slum dwellers. Fink et al. [16] noted that most of the health differences observed among residents of slums could be explained by differences in maternal education, family wealth, and access to health services. Chauhan and Dhar [17] reported that the mental health status of adolescents living in an informal settlement of India was correlated with gender, social class, education level, employment status, type of work, average monthly income, type of housing, and exposure to the media. Therefore, according to the reviewed studies, the socioeconomic status of the family is considered to be one of the most important dimensions of social determinants of slum dwellers’ health. The component of undesirable childhood experiences is also one of the most important social determinants of health, to the point that it could potentially be considered as a separate dimension; however, in this study, since it had common features with family status, it was included in this dimension.
- Proximity effects in neighborhoods that help create a healthy environment in slums are likely to be economically affordable and increase investment returns [3].
- In some of the reviewed studies conducted on slums, the neighborhood characteristics were addressed as an important factor affecting the health of slum dwellers. Silva et al. [18] confirmed the presence of a significant relationship between the neighborhood characteristics and mental health of slum dwellers. In another study [19] concluded that 4 important factors involved in the development of non-communicable diseases were a lack of clean water, inappropriate transportation system, inadequate physical activity, and low levels of education. Another study concluded that health promotion interventions through the creation of green spaces in slums had a significant impact on residents’ health [20].
- Nutrition, health behaviors, and occupational factors, as mentioned in the reviewed studies, are also important social determinants of health that should be considered in the health promotion programs designed for slum dwellers. The results of a study by Mondal et al. [21] showed that behavioral factors, such as tobacco and alcohol consumption, as well as insufficient consumption of fruits and vegetables, affected the prevalence of non-communicable diseases. It was found that food insecurity and lack of food resources were associated with the spread of acquired immune deficiency syndrome in slums [22]. In a study by Gruebner et al. [23], job satisfaction was reported to be among the factors affecting the mental health of slum dwellers.
- Pawar et al. [6] showed that social isolation and lack of social support were significantly associated with illness among slum dwellers. In another study, social support was reported to be an important social determinant of hypertension and diabetes among residents of slums [24]. Therefore, the dimensions and components identified in this study could be used as a framework for health promotion interventions designed for slum dwellers. This research is one of the first studies summarizing the results of various studies in this field. Given the common features of slums, there is a need for further research to identify other components and dimensions affecting the health of slum dwellers in order to compare these dimensions with those included in existing models and to clarify their differences and similarities. Since interventions based on social determinants of health require that different organizations play various roles in relation to health, it is suggested that more research should be conducted in the future to clarify the role of other organizations and institutions in promoting the health of these settlements’ residents to facilitate the design and implementation of urban programs and interventions in slums based on the proposed framework of social determinants of health with identified dimensions and components.
- One of the strengths of this study is the provision of an innovative integrated framework for promoting the health of slum residents, which could be useful and applicable in health promotion measures and intervention in these places. However, a limitation of this research is that only articles in English were reviewed. Moreover, the important dimensions and components of social determinants of health were classified based on their similarities, which need additional research to confirm, and it may be possible to present the classification in other forms as well.
DISCUSSION
- Given the importance of health as a human right, as well as the low-level of health among residents of slums or informal settlements in most parts of the world, it is recommended that interventions be designed and implemented in these areas within the framework of social determinants of health by taking into account the influential factors collected from the reviewed studies and presented herein. In addition to providing adequate and acceptable health services, special attention should be paid to social determinants of health in order to compensate for inadequacies in physical and mental health and to improve the health of these settlements’ residents, as well as to establish justice in health. Eventually, this framework could be used by planners, urban managers, and policy-makers when making decisions that affect the health of these settlements’ residents due to the common characteristics of slums around the world, especially in developing countries.
CONClUSION
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest associated with the material presented in this paper.
-
FUNDING
None.
Notes
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: MRG, FNN. Data curation: FNN, SHMK, SST. Formal analysis: MRG, RG. Funding acquisition: None. Methodology: RG, SHMK, MRG. Project administration: SST, MRG. Writing – original draft: MRG, RG. Writing – review & editing: FNN, RG, MRG, SHMK, SST.
Notes
| Study | Research location | Research method |
|---|---|---|
| Ezeh et al., 2017 [2] | Low-income and middle-income countries | Literature review |
| Lilford et al., 2017 [3] | Not stated | Systematic review |
| Weimann et al., 2019 [12] | Africa | Systematic review |
| Nekoei-Moghadam et al., 2019 [13] | Kerman, Iran | Semi-structured interviews. |
| Alaazi et al., 2020 [14] | Sub-Saharan Africa | Literature review |
| Subbaraman et al., 2014 [15] | Mumbai, India | Mixed methods |
| Fink et al., 2014 [16] | Developing countries | Secondary analysis |
| Chauhan et al., 2020 [17] | India | Cross-sectional study |
| Silva et al., 2016 [18] | Not stated | A review of the evidence |
| Lumagbas et al., 2018 [19] | India | Review of the literature |
| Korn et al., 2018 [20] | Lima, Peru | Longitudinal pilot study |
| Mondal et al., 2019 [21] | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Cross-sectional study |
| Steenkamp et al., 2014 [22] | South Africa | Cross-sectional study |
| Gruebner et al., 2012 [23] | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Cohort study |
| Parmar et al., 2019 [24] | India | Cross-sectional study |
| Soeung et al., 2012 [25] | Cambodia | Mixed methods |
| Gawde et al., 2013 [26] | Mumbai, India | Cross-sectional |
| Ahsan et al., 2017 [27] | Bangladesh | Secondary analysis |
| Booth et al., 2018 [28] | Chicago, USA | Secondary analysis |
| Ajlouni, 2016 [29] | Jordan | Pre-structured interview and focus group meetings |
| Corburn et al., 2015 [30] | Nairobi, Kenya | Mixed methods |
| Gadallah et al., 2017 [31] | Egypt. | Cross-sectional study |
| Rawal et al., 2017 [32] | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Cross-sectional study |
| Latif et al., 2016 [33] | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Mixed methods |
| Compton et al., 2015 [34] | Not stated | Narrative review |
| Khattak et al., 2016 [35] | Peshawar, Pakistan | Descriptive cross-sectional study |
| Fakir et al., 2015 [36] | Dhaka, Bangladesh | Logistic analysis |
| Panigrahi et al., 2017 [37] | Bhubaneswar, India | Cross-sectional study |
| Raju et al., 2019 [38] | Bangladesh | Secondary analysis |
| Unger, 2013 [39] | Not stated | Narrative review |
| Kyu et al., 2013 [40] | Low- and middle-income countries | Secondary analysis |
| Pandita et al., 2017 [41] | India | Observational study |
| Panigrahi et al., 2014 [42] | India | Cross-sectional study |
- 1. Owusu-Ansah FE, Tagbor H, Togbe MA. Access to health in city slum dwellers: the case of Sodom and Gomorrah in Accra, Ghana. Afr J Prim Health Care Fam Med 2016;8(1):e1-e7Article
- 2. Ezeh A, Oyebode O, Satterthwaite D, Chen YF, Ndugwa R, Sartori J, et al. The history, geography, and sociology of slums and the health problems of people who live in slums. Lancet 2017;389(10068):547-558ArticlePubMed
- 3. Lilford RJ, Oyebode O, Satterthwaite D, Melendez-Torres GJ, Chen YF, Mberu B, et al. Improving the health and welfare of people who live in slums. Lancet 2017;389(10068):559-570ArticlePubMed
- 4. Ompad DC, Galea S, Caiaffa WT, Vlahov D. Social determinants of the health of urban populations: methodologic considerations. J Urban Health 2007;84(3 Suppl):i42-i53ArticlePubMed
- 5. Alami A. Equity in health from social determinants of health’s point of view. J Res Health 2011;1(1):7-9. (Persian)
- 6. Pawar AB, Mohan PV, Bansal RK. Social determinants, suboptimal health behavior, and morbidity in urban slum population: an Indian perspective. J Urban Health 2008;85(4):607-618ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Ingram M, Schachter KA, Sabo SJ, Reinschmidt KM, Gomez S, De Zapien JG, et al. A community health worker intervention to address the social determinants of health through policy change. J Prim Prev 2014;35(2):119-123ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Solar O, Irwin A. A conceptual framework for action on the social determinants of health. 2010 [cited 2021 Jul 1]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241500852
- 9. World Health Organization. A conceptual framework for action on the social determinants of health. 2010 [cited 2021 Jul 1]. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/44489
- 10. Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med 2018;169(7):467-473ArticlePubMed
- 11. Munn Z, Peters MD, Stern C, Tufanaru C, McArthur A, Aromataris E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med Res Methodol 2018;18(1):143ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Weimann A, Oni T. A systematised review of the health impact of urban informal settlements and implications for upgrading interventions in South Africa, a rapidly urbanising middle-income country. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2019;16(19):3608ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Nekoei-Moghadam M, Heidari N, Amiresmaeili M, Heidarijamebozorgi M. Identifying the health problems of slum residents using social determinants of health: Kerman, Iran. Int J Health Plann Manage 2019;34(2):e1179-e1187PubMed
- 14. Alaazi DA, Aganah GA. Understanding the slum-health conundrum in sub-Saharan Africa: a proposal for a rights-based approach to health promotion in slums. Glob Health Promot 2020;27(3):65-72ArticlePubMed
- 15. Subbaraman R, Nolan L, Shitole T, Sawant K, Shitole S, Sood K, et al. The psychological toll of slum living in Mumbai, India: a mixed methods study. Soc Sci Med 2014;119: 155-69ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Fink G, Günther I, Hill K. Slum residence and child health in developing countries. Demography 2014;51(4):1175-1197ArticlePubMed
- 17. Chauhan SK, Dhar M. Prevalence and predictors of mental health disorder among the adolescent living in the slums of Lucknow, India: a cross-sectional study. Community Ment Health J 2020;56(3):383-392ArticlePubMed
- 18. Silva M, Loureiro A, Cardoso G. Social determinants of mental health: a review of the evidence. Eur J Psychiatry 2016;30(4):259-292
- 19. Lumagbas LB, Coleman HL, Bunders J, Pariente A, Belonje A, de Cock Buning T. Non-communicable diseases in Indian slums: re-framing the Social Determinants of Health. Glob Health Action 2018;11(1):1438840ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. Korn A, Bolton SM, Spencer B, Alarcon JA, Andrews L, Voss JG. Physical and mental health impacts of household gardens in an urban slum in Lima, Peru. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2018;15(8):1751ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. Mondal R, Sarke RC, Banik PC. Prevalence and determinants of behavioral risk factors of non-communicable diseases among a selected slum population in Bangladesh. Chronic Dis J 2019;7(3):170-174
- 22. Steenkamp L, Venter D, Walsh C, Dana P. Socio-economic and demographic factors related to HIV status in urban informal settlements in the Eastern Cape, South Africa. Afr J AIDS Res 2014;13(3):271-279ArticlePubMed
- 23. Gruebner O, Khan MM, Lautenbach S, Müller D, Krämer A, Lakes T, et al. Mental health in the slums of Dhaka - a geoepidemiological study. BMC Public Health 2012;12: 177ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Parmar VB, Rupani MP, Trivedi AV. Social determinants of diabetes and hypertension in an urban slum of Gujarat, Western India: a cross-sectional study. Online J Health Allied Sci 2019;18(1):1
- 25. Soeung SC, Grundy J, Sokhom H, Blanc DC, Thor R. The social determinants of health and health service access: an in depth study in four poor communities in Phnom Penh Cambodia. Int J Equity Health 2012;11: 46ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Gawde N, Nasirabadi M, Shah N, Nagaonkar S. Psychiatric morbidity in an urban slum of Mumbai: cross sectional study. Asian J Psychiatr 2013;6(6):478-482ArticlePubMed
- 27. Ahsan KZ, Arifeen SE, Al-Mamun MA, Khan SH, Chakraborty N. Effects of individual, household and community characteristics on child nutritional status in the slums of urban Bangladesh. Arch Public Health 2017;75: 9ArticlePubMedPMC
- 28. Booth JM, Teixeira S, Zuberi A, Wallace JM Jr. Barrios, ghettos, and residential racial composition: examining the racial makeup of neighborhood profiles and their relationship to self-rated health. Soc Sci Res 2018;69: 19-33ArticlePubMed
- 29. Ajlouni MT. Social determinants of health in selected slum areas in Jordan: challenges and policy directions. Int J Health Plann Manage 2016;31(1):113-125ArticlePubMed
- 30. Corburn J, Hildebrand C. Slum sanitation and the social determinants of women’s health in Nairobi, Kenya. J Environ Public Health 2015;2015: 209505ArticlePubMedPMC
- 31. Gadallah M, Megid S, Refaey S, El-Hussinie M, Mohsen A, Ardakani M, et al. The application of Urban Health Equity Assessment and Response Tool to assess health inequity among dwellers of an urban slum area in Giza Governorate, Egypt. J Egypt Public Health Assoc 2017;92(2):68-76ArticlePubMed
- 32. Rawal LB, Biswas T, Khandker NN, Saha SR, Bidat Chowdhury MM, Khan AN, et al. Non-communicable disease (NCD) risk factors and diabetes among adults living in slum areas of Dhaka, Bangladesh. PLoS One 2017;12(10):e0184967ArticlePubMedPMC
- 33. Latif MB, Irin A, Ferdaus J. Socio-economic and health status of slum dwellers of the Kalyanpur slum in Dhaka city. Bangladesh J Sci Res 2016;29(1):73-83Article
- 34. Compton MT, Shim RS. The social determinants of mental health. Focus 2015;13(4):419-425Article
- 35. Khattak M, Shah MU, Jan MS, Ali A, Ashiq S, James S. Health conditions of children and their socioeconomic determinants in slums: a study of Peshawar (Tajabad). J Med Stud 2016;2(3):4-10
- 36. Fakir AM, Khan MW. Determinants of malnutrition among urban slum children in Bangladesh. Health Econ Rev 2015;5(1):59ArticlePubMed
- 37. Panigrahi A, Panigrahi M, Padhy AP, Das SC. Common mental disorder and its socio-demographic correlates among married women residing in slum areas of Bhubaneswar, India. Women Health 2017;57(5):521-533ArticlePubMed
- 38. Raju D, Kim KY, Nguyen QT, Govindaraj R. Cities, slums, and child nutrition in Bangladesh. Rev Dev Econ 2019;23(2):760-781Article
- 39. Unger A. Children’s health in slum settings. Arch Dis Child 2013;98(10):799-805ArticlePubMed
- 40. Kyu HH, Shannon HS, Georgiades K, Boyle MH. Association of urban slum residency with infant mortality and child stunting in low and middle income countries. Biomed Res Int 2013;2013: 604974ArticlePubMedPMC
- 41. Pandita AK, Roy D, Saxena V. A study on morbidity pattern among geriatric population of an urban slum, Dehradun, India. Indian J Community Health 2017;29(4):402-409ArticlePDF
- 42. Panigrahi A, Das SC. Undernutrition and its correlates among children of 3-9 years of age residing in slum areas of Bhubaneswar, India. ScientificWorldJournal 2014;2014: 719673ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Deprivation and Its Association with Child Health and Nutrition in the Greater Kampala Metropolitan Area of Uganda
Rornald Muhumuza Kananura, Peter Waiswa, Ronald Wasswa, Ties Boerma, Cauane Blumenberg, Abdoulaye Maiga
Journal of Urban Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - “For my safety and wellbeing, I always travel to seek health care in a distant facility”—the role of place and stigma in HIV testing decisions among GBMSM – BSGH 002
Edem Yaw Zigah, Gamji Rabiu Abu-Ba'are, Osman Wumpini Shamrock, Henry Delali Dakpui, Amos Apreku, Donte T. Boyd, LaRon E. Nelson, Kwasi Torpey
Health & Place.2023; 83: 103076. CrossRef - Identifying, Measuring, and Ranking Social Determinants of Health for Health Promotion Interventions Targeting Informal Settlement Residents
Farhad Nosrati Nejad, Mohammad Reza Ghamari, Seyed Hossein Mohaqeqi Kamal, Seyed Saeed Tabatabaee
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(4): 327. CrossRef - Do Community-based Livelihood Interventions Affect Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights of Young People in Slum Areas of Uganda: a Difference-in-difference with Kernel Propensity Score Matching Analysis
Andre M. N. Renzaho, Joseph K. Kamara, Daniel Doh, Paul Bukuluki, Rashidul A. Mahumud, Moses Galukande
Journal of Urban Health.2022; 99(1): 164. CrossRef
 KSPM
KSPM


 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite